Free Course Notes
Understanding Cyber Security
What is Cyber Security?
The term ‘cyber security’ refers to all safeguards and measures implemented to reduce the likelihood of a digital security breach
Focus on privacy, confidentially, data integrity and identity protection.
Costs
- Reputational damage
- System downtime
- Financial loss
The Importance of Security
Much business n stuff on the internet, and continues to grow.
Protecting the business is not enough. We have a legal obligations to protect our customers too.
Insiders And Outsiders
As far as general data security is concerned, there are two classifications of people – insiders and outsiders (aka employees and non-employees). Figure Intro shows the three classes of computer security and crime caused by each of the two types, plus a special class of threats that are not directly caused by humans, namely accidents.
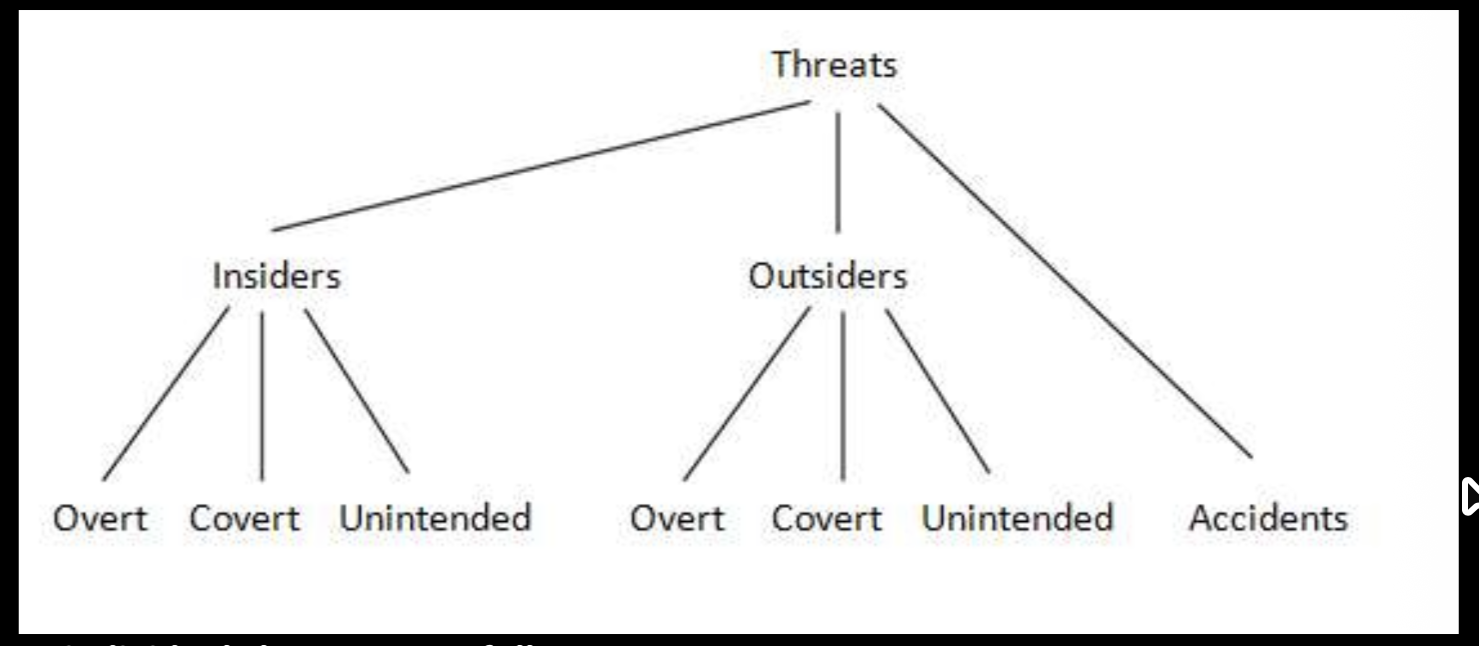
The seven individual classes are as follows:
- Insiders overt. Overt actions on the part of insiders are usually the work of dissatisfied employees, often resulting in data being compromised and equipment being destroyed.
- Insiders covert. Employees within a company can inflict more serious damage than outsiders, due to their access privileges and extensive knowledge of the organiSation in general.
- Insiders unintended. Many security issues or threats that occur internally are the result of nothing more than genuine human error. This being one of the most common threat classes.
- Outsiders overt. Direct attacks on network systems and computer facilities by outsiders, which also incorporates DoS attacks. -Denial of Service
- Outsiders covert. This refers to the type of attack that involves transmitting rogue software to one or more computers or systems from outside the business.
- Outsiders unintended. It is fairly rare that an outsider will harm a computer or access sensitive data unintentionally.
- Accidents. Issues regarding data integrity or security can arise due to unpredictable accidents that cannot be prevented, such as natural disasters, workplace fires and so on.
Three Main issues/threats
- Physical Security. include computer equipment being stolen, computer systems being accessed physically without authorisation and general physical damage being caused to hardware.
- Rogue Software. includes all examples of computer viruses and malware. Any software introduced to a system (accidentally or otherwise) that poses or creates a security threat.
- Network Security. The vast majority of computers these days are connected to one or more networks, which may be breached by insiders or outsiders. When a network is accessed or in any way compromised without authorisation, this is considered a network security issue
there is no such thing as 100% flawless protection from attacks Constantly new/refined techniques. Perpetual cat n mouse on both sides
Microsoft’s 10 Laws of Cyber Security:
The 10 rules outlined by Microsoft are as follows:
- If someone can persuade you to run their program on your computer, it’s not your computer anymore.
- If someone can alter the operating system on your computer, it’s not your computer anymore.
- If someone has unrestricted physical access to your computer, it’s not your computer anymore.
- If you allow someone to upload anything it’s a to your website, it’s not your website anymore.
- Weak passwords defeat strong security.
- A computer is only as secure as its owner/user is trustworthy.
- Encrypted data is only as secure as the decryption key.
- An out-of-date virus scanner is only marginally better than none at all.
- Absolute anonymity isn’t practical, in real life or on the Web.
- Technology is not a panacea.